Blockchain is a growing ‘forest’ of trust, cyber safety, audit and regulations for securing the best, transparent and safest records.
Blockchain is a shared, immutable ledger that facilitates the process of recording transactions and tracking assets in a business network – which can be both tangible (a house, car, cash, land) or intangible (intellectual property, patents, copyrights, branding).
Blockchain helps in the verification and traceability of multistep transactions needing verification and traceability, by providing secure transactions, reducing compliance costs, and speeding up the data transfer processing. Blockchain technology can also help contract management and audit the origin of a product.
Blockchain as an emerged technology, contains almost daily upgrades, evaluations, assessments and involvements on its usage and applicability to everyday life across multiple domains.
As a platform, blockchain is perceived to provide significant opportunities to disrupt traditional products and services due to the distributed, decentralised nature and features such as the permanence of the blockchain record, and the ability to run smart contracts. These features make blockchain technology-based products or services significantly different from previous internet-based commercial developments.
Currently stakeholders within multiple sectors are largely unaware of the social advantages and potential of blockchain technology. The technology-based products and releases are documented and produced to create an awareness of this gap and not as a case study.
Blockchain maturity models (BMM) are evolving and playing a key role in providing organisations with the needed assessment criteria and evaluation parameters to explore the migration of existing technology platforms to Blockchain based services. This benefits end users from every domain with data transparency and audit capabilities.
Blockchain will be an incorruptible digital ledger of every transaction that can be programmed to record not just transactions, but virtually everything of value from every domain.
Blockchain technology is forecasted to disrupt any field of activity that is founded on any transaction or record which was created, exchanged, modified or deleted in printed or digital form, that shows the time some actions had taken place.
An illustration of some selective domains mentioned below on Blockchain impact will be advantageous for such providers.

A global trend in the third quarter of 2022 as depicted below has provided the outcomes and value creation as a ‘core and mandatory’ need for every transactional user who is looking to benefit due to the advantages seen, while implementing a Blockchain platform.
1. Enhance transparency to end users
a. Centralised ledgers are blockchains offering transparent, verifiable records for every transaction, both validating underlying other forms of fraudulently duplicated value.
2. Reduce threats of hacking
a. Data that exist in the blockchain are encrypted, making the information of little value for coercion, extortion or corporate espionage.
3. Increase patient record safety
a. Efforts to hack or change the ledger will be rejected by the broader network.
4. Eliminate workaround
a. Eliminate ICT workaround processes and provide an effective streamlined workflow benefitting every end users.
5. Minimise IT spend & downtimes
a. High-value machines cost millions. Downtime for them is not only very costly for organisations and facilities but also, more importantly, interrupts end users from getting best possible outputs or would rather say “Value”.
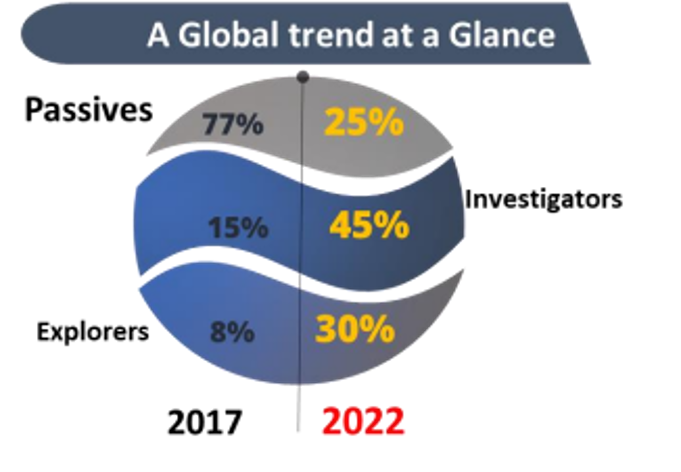
Every domain is undergoing a major shift and moving to next generation implementations towards data management, as illustrated by the global trend, with a shift over recent times from passive technology adopters towards more investigators and explorers.
There is a vital need for a universal transparent record in a distributed ledger and new approaches to ensure collaborative data when we can manage our own transactions outside of the system to improve outcome and contain ICT costs.
As a promising and proven breakthrough, such implementations have yielded that end users requirements and needs can be delivered through advanced techniques which will bring down late detection of failures by various advanced support systems and self-management tools.
Radhakrishnan M is a Chief Technology Advisor and Innovation / Growth Leader in multiple Blockchain initiatives and emerging technologies. He also the Chapter Lead for Government Blockchain Association (GBA) headquartered in the US.
The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of Doha News, its editorial board or staff.







