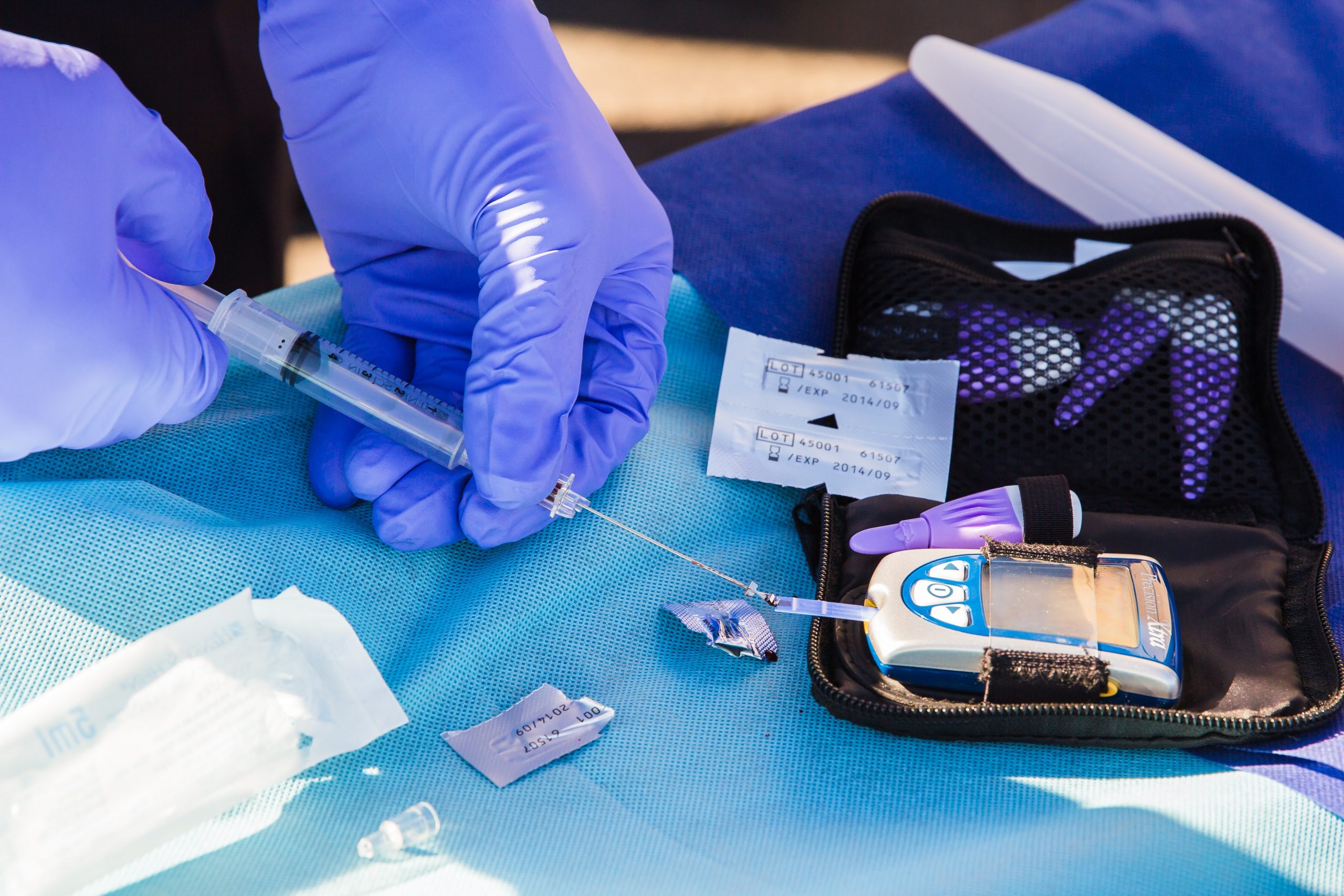
A total of 1.5 million deaths are also directly attributed to diabetes every year.
One in 20 new cases of diabetes could be linked to Covid-19 infection, a new study published by JAMA Network found.
Published on Tuesday, the study’s findings are based on an evaluation of 629, 935 individuals who had tested for Covid-19, with the median age of 32 years.
“In this cohort study, SARS-CoV-2 infection was associated with a higher risk of diabetes and may have contributed to a 3% to 5% excess burden of diabetes at a population level,” the study said.
The researchers looked into data from the British Columbia Covid-19 Cohort, which falls under the British Columbia Centre for Disease Control, and excluded those who had diabetes before testing positive or Covid-19.
Covid patients who were hospitalised had also greater risk of developing diabetes.
“Diabetes has already been established as a risk factor associated with more severe COVID-19 respiratory outcomes, and SARS-CoV-2 infection was associated with the worsening of preexisting diabetes symptoms,” the study explained.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), at least 422 million people globally have diabetes, most of which live in low and middle income countries. A total of 1.5 million deaths are also directly attributed to diabetes every year.
In Qatar, around 17% of the country’s population has been diagnosed with diabetes. An estimate of 10% of the Gulf state’s total deaths is linked to diabetes.